#Pharma1- Which of the following statements is false?• A. Diazepam has low lipid solubility.• B. Diazepam has active metabolites.• C. The actions of diazepam may be reversed by flumazenil.• D. Diazepam does not require adjustment in patients with chronic renal disease
#Pharma2- Which of the following is not a side effect of opioid administration?:• A. Mydriasis.• B. Respiratory depression.• C. Constipation• D. Nausea
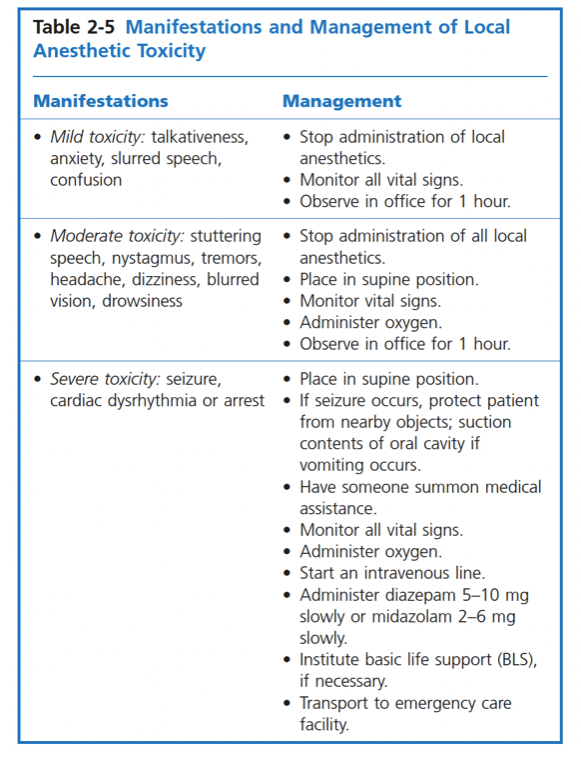
#Management3- Immediately after the administration of an inferior alveolar nerve block to start the root canal treatment on tooth 3.7, the patient complained of dizziness, nervousness, increased heart rate, which of the following the most likely diagnosis?
◯A. Local anesthetic toxicity.◯ B. Epinephrine Reaction.◯ C. Syncope.◯ D. Cardiac arrhythmia.
◯A. Local anesthetic toxicity.
#Pharma4- Which of the following is true regarding the management of a patient who is receiving warfarin and a history of pervious cerebrovascular accident?
◯ A.Non-surgical procedures should only be performed after consultation with the physician and INR below 2.5.◯B. Minor surgical procedures can be performed after consultation with the physician and INR below 3.5.◯ C. Major surgical procedures should only be performed after consultation with the physician and INR below 3.5.◯ D. Minor and major surgical procedures should be avoided until the patient is no longer taking warfarin.
◯ A.Non-surgical procedures should only be performed after consultation with the physician and INR below 2.5.
#Pathology5- Necrotizing sialometaplasia:
◯A. Is a premalignant condition.◯ B. Presents as a painful ulcer in the palate.◯ C. Does not require surgical excision.◯ D. All of the above.
◯A. Is a premalignant condition.
Join our AFK Weekly newsletter
Solving questions is really important, but solving exam grade questions with true and authenticated answers is critical.
Will post a question everyday, then at the week end will do a video to explain the correct answers and the concept of each questions, signup now to get weekly updates.
Will post a question everyday, then at the week end will do a video to explain the correct answers and the concept of each questions, signup now to get weekly updates.
Thank you!